Dry skin
Author: Hon A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, 1997. Update: March 2022.
What is dry skin?
Dry skin that begins later may be seen in people with certain diseases and conditions, such as:
- Postmenopausal females
- Hypothyroidism
- renal disease
- Malnutrition and weight loss
- Subclinical dermatitis
- Treatment with certain drugs such as oral retinoids, diuretics and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors.
People exposed to a dry environment may experience dry skin, for example:
- Low humidity : in desert climates or cool, windy conditions
- Excessive air conditioning
- Direct heat from a fire or fan heater
- Excessive bathing
- Contact with soap, laundry detergents and solvents
- Inappropriate topical agents such as alcohol
- Frictional irritation from rough clothing or abrasives.
What causes dry skin?
The inherited forms of ichthyosis are due to loss of function genes (listed in parentheses below):
- Ichthyosis vulgaris (FLG)
- Recessive X-linked ichthyosis (STS)
- ichthyoses (KRT1, KRT10, KRT2).
Acquired ichthyosis may be due to:
- Metabolic factors: thyroid deficiency
- Illness: lymphoma , internal sarcoidosis, HIV infection
- Drugs: nicotinic acid, kava, protein kinase inhibitors (eg EGFR inhibitors), hydroxyurea.
What are the clinical features of dry skin?
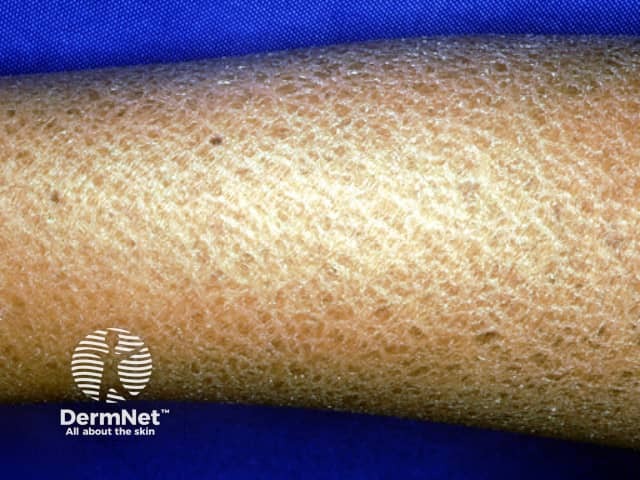
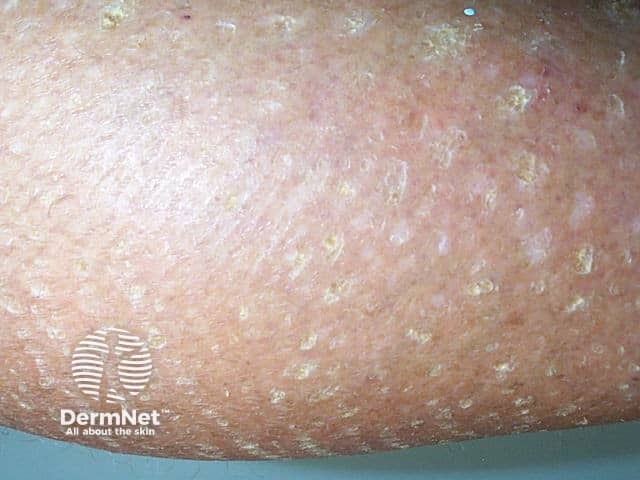
Close-up of ichthyosis
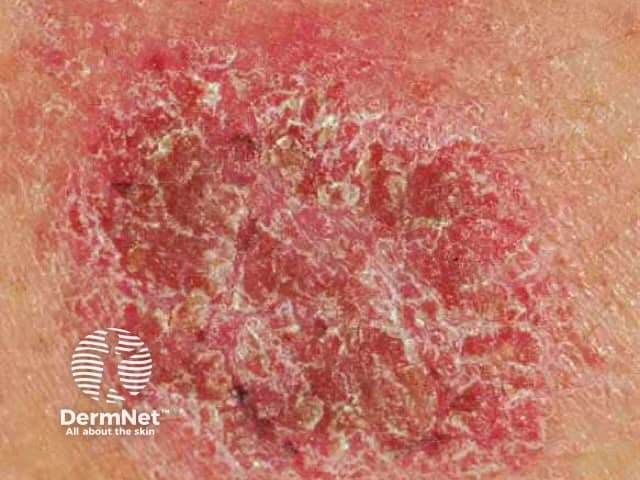
Complications of dry skin
Dry areas of skin may become itchy, indicating a form of eczema/dermatitis has developed, such as:
- Atopic eczema — especially in people with ichthyosis vulgaris
- Eczema craquelé — especially in older people. Also called asteatotic nummular dermatitis/discoid eczema — especially in people that wash their skin excessively.
When the skin of an older person is dry and itchy without a visible rash , it is sometimes called winter itch, 7th age itch, senile pruritus or chronic pruritus of the elderly.
Other complications may include:
- Flaky skin or itchy skin (pruritus)
- Skin infection when bacteria or viruses penetrate a break in the skin surface
- Overheating, especially in some forms of ichthyosis
- Food allergy, eg, to peanuts, has been associated with filaggrin mutations
- Contact allergy, eg, to nickel, has also been correlated with barrier function defects.
How is the type of dry skin diagnosed?
The type of dry skin is diagnosed by careful history and examination.
What is the treatment for dry skin?
- Reduce itch
- Improve the barrier function
- Prevent entry of transepidermal water loss.
When considering which emollient is most suitable, consider:
- Severity of the dryness
- Tolerance
- Personal preference
- Cost and availability.
How can dry skin be prevented?
- Eliminate aggravating factors.
- Reduce the frequency of bathing.
- A humidifier in winter and air conditioner in summer.
- Compare having a short shower with a prolonged soak in a hot bath.
- Ensure good hydration by drinking plenty of water.
- Use lukewarm water, not hot water.
- Replace standard soap with a substitute such as a cleanser, water-miscible emollient, bath oil, anti- oatmeal etc.
- Apply an emollient liberally and often, particularly shortly after bathing, and when itchy. The drier the skin, the thicker this should be, especially on the hands.




